CASE STUDY
Development of an IHC-Based Assay for Detection Of P-Cadherin in Tumor Tissue
Clinical Application: Patient Selection for Enrollment
Key Words: patient stratification, tumor biopsies, quantitative IHC
Background: Personalized medicine is an emerging idea in health care; the ability to determine a patient’s responsiveness to a given treatment in advance, through real-time testing, would be useful for many. In this particular case, ApoCell helped to assess the feasibility of using an immunohistochemical (IHC) assay for P-cadherin, a cellular adhesion protein that is thought to contribute to the oncogenesis of many types of cancers, as a means of patient selection for an ongoing Phase I clinical trial. Each patient’s P-cadherin expression level was then quantified using immunofluorescence (IF), and was evaluated as a correlative measure with clinical outcome.
Methods: ApoCell first tested and finalized an IHC assay and reagent kit that would be used by each trial site for testing. Tumor biopsies were then obtained from 94 patients, from three sites world-wide. Each trial site ran independent IHC assays using kits provided by ApoCell, conducted analyses by board-certified pathologists, and provided both their IHC-stained slides and additional unstained archival biopsy slides for analysis by ApoCell. A scoring index (SI) was used to evaluate P-cadherin positivity (see Figure 1); an SI of greater than or equal to 4 was associated with poor clinical outcome, and was chosen as one criterion for inclusion into the trial.
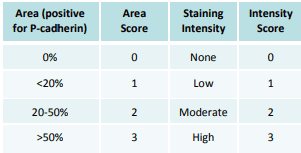
Figure 1. SI for P-Cadherin staining.
IHC slides were scored for P-Cadherin positivity using a product of the area score (a measure of the total tumor tissue positive for P-Cadherin) and the intensity score (a measure of staining intensity. An SI of greater than or equal to four was chosen as one of the criteria for inclusion into the trial.
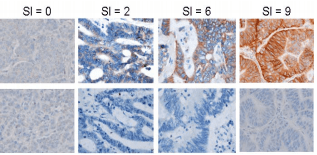
Figure 2. Representative Imager of P-Cadherin IHC Staining.
The images above illustrate typical images of P-Cadherin staining at the specified SIs. The top row represents P-Cadherin stained-tissue; the bottom row represents examples of paired negative controls.
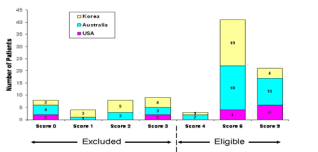
Figure 3. P-cadherin IHC Scoring Summary. Using the SI system,
a total of 65 of 94 (69.2%) patients were found to be P-cadherin
positive, and thus eligible for inclusion into the trial. Good agreement (86 of 94 patients; 91.5% concordance rate) was
found in the scoring of the IHC slides between the trial sites and ApoCell, indicating consistency and reproducibility of the method for future applications.
Impact: This study indicates the feasibility of prospectively selecting patients based on IHC expression of P-cadherin using a custom standardized scoring index analysis across
multiple clinical sites. It also indicates that such methods could theoretically be applied to other biomarkers and other cancer types as well. Being able to analyze the expression
levels of certain biomarkers – specifically, examining particular drug targets, and evaluating the efficacy of a treatment prior to administering it – within a patient’s tumor with
relative haste could easily lead to an improvement in many patients’ prognosis.
References: 1. Davis DW, et al. “Prospective Real-Time Analysis of P-cadherin Expression to Select Patients into a Phase I Oncology Trial.” EORTC-NCI-AACR, 2009.